Server Properties
The Server properties area is the main area for server configuration. It is divided into the following categories:
- General
General Parameters / Login / DMS Options / Security / Workflow / Conversion / Subscription/Follow-up / Client Options
- Services
Content Processing Bus / Rendition Cache / Contentviewer / Documentviewer / Appconnector / Web service / Exchange / IMAP / Full Text / Gateway / Discovery / Dashlets 1–10
When you open this area, you will have to refresh the view. Alternatively, you can activate the Refresh at connection option.
Category: General
For simplicity's sake, data in the General category is divided into further areas. The following settings are available in this category:
General Parameters
|
Parameter |
Default (registry entry) |
Description |
|
ComString |
(ComString) |
The IP address or host name of the computer on which the server is running or, if a cluster solution is used, the cluster IP address. This address is entered during installation and added to the registry. This entry must only be changed for cluster solutions. If used, enter the cluster IP address via which clients can reach the clustered server. |
|
TCP port |
(TCPPort) |
The TCP port of the server instance. The port is entered during installation and added to the registry. If you change the port number, you will need to modify this entry accordingly. |
|
Crash timeout |
300 seconds (CrashTimeout=300) |
Defines the time in seconds after which a server blackout is assumed if the alive signal is not being transmitted. This entry will be ignored unless multiple servers are used. The alive signal is sent by the periodic job 'BeatPing/Serverping'. The timeout value must be greater than the value for the periodic job. The corresponding sessions will be imported if the timeout expires and a server failure is suspected. |
|
Maximum number of TCP sockets |
1500 (MaxConnections=1500) |
The maximum number of TCP sockets that the server opens for connection requests. If the computer's memory utilization is too high, you can reduce it by lowering this value. However, at least four TCP sockets are required for each client. |
|
Timeout for the start of a job thread |
10000 milliseconds (Threads\JobStartTimeout=10000) |
The time provided for a job thread to start. After this timeout, an attempt is made to start a new job thread. Only increase the time period temporarily in order for you to determine whether job threads, which could not start due to a timeout, may be started then. |
|
Wait before launching |
0 seconds (WaitSec=0) |
Number of seconds the server waits before it launches. A waiting period may be necessary if the server has to wait for a database or full-text server. |
|
Free disk space |
50 MB (Archive\MinDiskSpace=50) |
The minimum free disk space in the work area, in the server installation directory, and in the configured server log directory. The server service will not start if this minimum space is not available in one of these areas. We recommend increasing this value. Large documents or extensive logging may quickly fill up this space. During ongoing operation, periodic jobs determine the remaining free disk space. If a configurable size is not reached, an e-mail is sent to the administrator's account with a corresponding message. By default, these periodic jobs are activated and use the minimum available disk space entered here as the default value. |
|
E-mail if not found on main medium |
Not active (Archive\ |
Defines whether or not to send an e-mail to the administrator's account if a document was only found on the mirrored medium but not on the main medium. Such errors should always be analyzed. The administrator's e-mail data must be available (see below). |
|
Job execution without login |
Allowed (LoginForJobs=1) |
Defines whether or not to perform server jobs of clients which have not yet logged on. |
|
Always close sessions |
Close sessions (KillSessionOnDisconnect=1) |
Turns on or off reservation of sessions. Sessions should not be reserved. |
|
Reservation time |
0 seconds (SessionPreserve=0) |
Defines how long a canceled session will remain reserved for later recovery (in seconds). Sessions should not be reserved. The reservation time is only relevant if sessions are reserved. |
|
Computer name |
- (ComputerName) |
If specified, this name is used to identify the application server in the 'server' table. This entry must remain empty. |
|
Memory size for compression and extraction |
50 MB (Archive\MaxCabMemory=50) |
Maximum size (in MB) of the file which is compressed/extracted in the memory; otherwise, the hard disk is used. |
|
Path to access log |
- (AccessProtocol) |
The path to the access log. An access log will not be created if nothing is entered here. |
|
Use hard links |
Use (Switches\DoCopy=0) |
Defines whether to copy document files or create hard links, especially in the WORK/CACHE directory. If hard links cannot be created, the files will be copied. The server checks at start whether it is possible to create hard links. If not, an error message will be written to the start log. The creation of hard links can be generally deactivated via the following registry key: Archive\DoNotUseHardLinksSet the value to '1' to not check and to not create hard links. |
|
Administrative e-mails |
Allow e-mails (NoMails=0) |
Disables or enables the sending of administrative e-mails for the transfer of system events. The log files 'startup.txt' and 'shutdown.txt' are also sent during startup and shutdown. |
|
E-mail address of the administrator |
- (AdminMail) |
E-mail address of an administrative account for the transfer of system events (server start/end) by the server. Use the semicolon to separate multiple e-mail addresses. |
| E-mail address of the help desk |
- (HelpDeskEmail) |
E-mail address of an administrative account for the transfer of system errors by the user. For example: error messages from add-ins. |
|
E-mail server |
- (MailServer) |
The IP address or host name of the e-mail server for administrative e-mails. |
|
E-mail sender |
- (MailSender) |
The sender's name or address to be given to the server when sending e-mails to an administrator's account. 'askrn' is used by default if this entry is left empty. |
|
SMTP server port |
25 (SMTPPort=25) |
Port for SMTP |
|
SMTP NTLM domain |
- (SMTPNtlmDomain) |
Defines the NTLM domain for authentication with NTLM. |
|
SMTP authentication |
None (SMTPAuthenticating=0) |
Authentication method for SMTP. |
|
SMTP user name |
- (SMTPUserName) |
User name for SMTP login. |
|
SMTP password |
- (SMTPPassword) |
Password for SMTP login. The password will be encrypted prior to storage and then masked when shown. |
|
SMTP encryption |
0 (SMTPSecurity=0) |
None (0), SSL (1), TLS (2). The corresponding port must also be set during encryption. |
| Microsoft Office client ID |
- (OfficeClientID) |
Office 365 client ID for the e-mail authentication 'OAuth2 Microsoft Office'. |
| Microsoft Office client secret |
- (OfficeClientSecret) |
Office 365 client secret for the e-mail authentication 'OAuth2 Microsoft Office'. The client secret will be encrypted prior to storage and then masked when shown. |
| Microsoft Office tenant ID |
- (OfficeTenantID) |
Office 365 tenant ID for the e-mail authentication 'OAuth2 Microsoft Office'. In addition to the registry entries OfficeClientID, OfficeClientSecret, OfficeTenantID, SMTPUserName, MailSender, MailServer, and SMTPPort, further registry entries are included for the e-mail authentication 'OAuth2 Microsoft Office'. These should generally only be changed after consultation: OfficeTokenEndpoint, OfficeAccessScopes, OfficeTokenGraceTimeInSeconds. |
|
NetSend address |
- (AdminNet) |
The name of the computer to which administrative messages are sent with NetSend. If this entry is empty, NetSend messages will not be sent. |
|
NetSend sender |
- (AdminName) |
The name of the sender for NetSend messages. A sender is optional. |
|
Monitoring license utilization |
90 (LicenseThreshold=90) |
Enter a value defining license utilization in percent – if this value is exceeded, an e-mail is sent to the administrator's account. Enter the value '0' to not monitor the license utilization. Details about monitoring can be found in the section 'Detecting Licenses'. |
|
E-mail about license utilization |
Send (LicenseThresholdMail=1) |
Defines whether or not to send an e-mail to the administrator's account if the value defining the license utilization is exceeded. An exceeding of the utilization value will be written to the flow log if the log level is set to 3. |
| Path for the online help |
- (HelpURL) |
If the online help is to be installed locally on the intranet or file system, specify the first part of the path here. Call structure: https://help.optimal-systems.com/enaio/v1110/... Your local online help must be accessible under: <HelpURL>/v1110/... The online help for local access is available on request. |
Login
In order to log in, every user must enter his or her user name and password into the enaio® user administration system.
If you have chosen NTLM authentication and set up NTLM authentication in the operating system, users who have been imported into the enaio® user administration system as NT users can log in with their Windows user name and password. The users and servers must always belong to the same domain.
If the activated NTLM authentication fails when enaio® enterprise-manager is started, then no further authentication will be carried out.
If a password confirmation is required for follow-ups, subscriptions, workflows, or a script by the user, then, by default, the user name and the enaio® password must be entered, even if NTLM/Kerberos authentication is enabled.
If NTLM/Kerberos authentication is used in combination with a login sequence (see below), then the login types listed there will be used in that order for verification. If 'A' is entered there in the first position, then the Windows password can be used for the confirmations in enaio® client.
For enaio® webclient, the confirmation must be specifically configured.
Confirm with password can be deactivated for enaio® client.
Standard authentication is available, enabling users to log in with the enaio® user name and enaio® password. If the Windows user name corresponds to the enaio® user name, you can allow users to automatically login via the operating system.
If an LDAP server provides the user names, activate auto login and set the login mode to 'LDAP' in order to enable automatic login via the operating system using the login data. Users who have been signed out from the LDAP server will not be able to log in anymore, even if they are still registered as enaio® users. In LDAP mode, the login dialog prompts users to enter their LDAP user name and their enaio® password.
Anonymous access to the LDAP directory service is not generally allowed; as a result, authentication at the LDAP system is required for identification of LDAP users and their rights. To do so, you will need an LDAP user with the appropriate rights. Enter your user name and password on the 'LDAP Configuration' Tab in enaio® administrator.
You can also specify a login sequence for standard authentication.
|
Parameters |
Default (registry entry) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Auto login |
Not active (Login\AutoLogin=0) |
Allows auto login in standard authentication mode using the operating system's login data. |
|
SSP login |
Not active (Login\NTLMLogin=0) |
Allows server-side or Windows-side authentication via the user name and password. Standard authentication is carried out using the enaio® user name and enaio® password, or in LDAP or Active Directory (see below). |
| Security Support Provider |
- (Login\SecuritySupportProvider) |
Specifies which Windows-side security support provider is used for login: Kerberos or NTLM A Kerberos authentication requires additional settings. |
| Name resolution (Kerberos) |
- (Login\QueryNamesMethod) |
Specifies whether the enaio® user name is set using the SAM account name (SAM) or the user principal name (UPN) of the Windows user who is logging in when using Kerberos. Another value is possible for Kerberos name resolution: UPN via LDAP. The UPN is determined using the security ID via the LDAP connection. This value may be necessary in complex AD architectures built on several subdomains. Currently, this value must be set via the registry. Login\QueryNamesMethod: value: 2 |
|
Login mode |
Dialog (Login\LoginMode=0) |
Defines whether the user is logged on via enaio® user administration, LDAP, or Active Directory (Dialog/LDAP/Active Directory) if standard authentication is used. If a login order has been defined, this value will be ignored. |
|
Login order |
- (Login\LoginPipe) |
If multiple login types are possible, list them here in the intended order. |
|
Check case sensitivity of passwords |
Do not check case sensitivity (Login\PwdCaseSensitive=1) |
Specifies whether or not to check the case sensitivity of passwords in standard authentication mode. In NTLM authentication mode, the operating system setting takes precedence. |
|
Computer identification |
Name (Station\Ident=name) |
The modules can be assigned to the computers via the names or GUID. When installing terminal servers, the GUID must be used for identification because the names may differ. This setting requires that the GUID has been used for licensing and that every computer that logs in has exactly one network card and can be identified. |
|
Change computer name |
Do not change (Station\ChangeName=0) |
If computer identification is performed by using the GUID; a modified computer name can be automatically updated for the license management view. This update is not obligatory. |
|
Security level |
No restriction (Login\SecurityLevel=0) |
Specify whether or not to close the application and to additionally lock the user account after three failed login attempts. This setting does not apply to users with two-factor authentication. |
|
Domain |
- (ValidDomains) |
Specifies the additional domains that the user must belong to in order to automatically log in to the server (auto login). Enter multiple servers, each separated by semicolon. Any user that belongs to the same domain as the server can always log in automatically. |
|
Active Directory domain |
- (Login\LoginDomain) |
Specifies which domain of the servers will be used to log in the user in Active Directory authentication mode. |
|
LDAP binding |
- (Login\LDAP\Binding) |
Enter the binding string which describes a particular position within the structure of the LDAP directory service which forms the starting point for search requests. When specifying more than one LDAP server above, you can also enter multiple binding strings separated by a semicolon. |
|
LDAP host |
- (Login\LDAP\Host) |
Indicate the LDAP server and, separated by a colon, its port number. Enter multiple LDAP servers separated by semicolon. Data of the LDAP server that is reached at first will be used for user administration. LDAP configurations are also possible via enaio® administrator and connections can be tested there. |
|
LDAP user attribute |
- (Login\LDAP\UserAttrib) |
Enter the LDAP attribute that is used as a unique user name. |
| LDAP version |
3 (Login\LDAP\Version) |
LDAP version Version 3 |
| LDAP security |
0 (Login\LDAP\UseSSL) |
LDAP security settings:
|
|
- (Login\PwdComplexity) |
Enter a regular expression in order to specify the password syntax which must be followed when allocating and changing passwords. If a password does not follow this syntax, it will not be accepted. You can test regular expressions in enaio® administrator. |
|
|
Description text for the password syntax |
- (Login\PwdComplexityDescription) |
A description of the syntax requirements which is displayed in the dialogs when allocating or changing passwords. |
|
Validity period of passwords |
0 (Login\PasswordExpirationInterval) |
Enter a time period in days which a password is valid for. The value '0' turns this function off. |
|
Notification when the period of validity expires |
5 (Login\PasswordExpirationWarning) |
Enter a value in days after which the user is notified about password expiration. |
| One-time password |
0 (Login\PasswordSingleUse) |
New users are created using a one-time password, and they must change their password immediately when logging in to enaio®. Only applies to server-side authentication. Changes only affect users who are created subsequently. |
| Two-factor Authentication |
0 (Login\EnableMFA) |
activates two-factor authentication. If two-factor authentication is activated (1), it can be configured individually for each user. |
|
Version check at server connection |
Minor (Login\CheckVersion) |
A version check can be carried out each time a client connects to enaio® server. If the versions do not match on the configured layer, enaio® server will not authorize the connection. Major releases, minor releases, or service pack versions can be validated. By default, the minor release version is checked. In order to make sure that no errors occur due to differences between versions, you can set an additional check to validate the SP version. |
|
User name for LoginPipe exceptions |
- (Login\AlternativeUserNames) |
Specify the users to be logged in using the alternative LoginPipe, such as the technical users. Use the semicolon to separate multiple user names. The '*' entry logs in all users using the alternative LoginPipe. In addition to specifying users, you will also need to enter the IP address of the computer on which the enaio® service is running using the 'IP addresses for LoginPipe exceptions' parameter. Furthermore, the 'Server: Switch job context' system role must be assigned to the users; otherwise, the program cancels the login operation with an error. |
|
IP addresses for LoginPipe exceptions |
- (Login\AlternativeIPAddresses) |
Specify the IP addresses to be used for the alternative LoginPipe. Use the semicolon to separate multiple IP addresses. It is recommended that you only specify the IP addresses of computers on which enaio® services are run. In addition to the IP address, you must also set the parameter 'User names for LoginPipe exceptions' to specify the user name under which the enaio® service runs. |
|
Alternative LoginPipe |
- (Login\AlternativeLoginPipe) |
As with 'login order' described above, you can specify an order for the LoginPipe exception. Only one entry is possible here as well. Use the following abbreviations: L=LDAP; A = Active Directory; I=User administration with password; U=User administration without password. |
DMS Options
|
Parameter |
Default (registry entry) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Limit on queries |
0 (DMSOptions\RequestRowsetLimit=0) |
Defines the maximum of records which may be returned by a server query. An error message is output if more records are found. Enter '0' to specify 'no limit'. You may only impose limits on the engine in consultation with the consulting team. Limits may also restrict the execution of automatic actions, for example, the 'Hash check on object level' and 'Dearchiving' actions. The limit on queries can be changed to run actions via the query file of the actions. |
|
Use station name for checkout |
No (DMSOptions\ |
Defines whether or not to identify the station based on its name for checkout. This may be required if stations cannot be clearly identified via their IP or GUID which will thus lead to check-in errors. |
|
Local date format |
No (DMSOptions\ |
No: User selects between German, English, and French. Note: The British date format is used for English and French: (DD/MM/YYYY). Yes: Follows the date and time format based on the settings of the local user on the workstation. Note: enaio® webclient, enaio® webclient as a desktop application, and enaio® mobile do not follow the local user settings and therefore do not observe the British date format for English and French. |
|
Local number format |
No (DMSOptions\ |
No: User selects between German, English, and French. Yes: Follows the number format based on the settings of the local user on the workstation. |
Security
|
Parameter |
Default (registry entry) |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Encrypted data area |
Encryption not active (Archive\CryptoStorage=0) |
Governs whether or not to use AES 256 encryption across the entire data area (work, cache, and archive). |
|
|
Disable user rights at job calls |
Only administrators (Security\ |
Defines which users are allowed to set the flag 'Do not check user rights' when executing jobs. 'Administrators' are users with system roles. Use script to carry out jobs and deactivate the check of user rights to increase system performance. Unfortunately, this creates a security vulnerability. For that reason, it is recommended to only grant this function to administrators. To completely close this security gap, set the value to 'Nobody'. |
|
|
Hashed communication |
No (Security\ |
Governs whether enaio® server accepts only jobs with a hash value. The oxmljsc.cfg configuration file allows you to change the respective setting for clients. By default, jobs are transferred with hash values. The file is found in the respective application directories. |
|
|
Compressed communication |
No (Security\ |
Governs whether enaio® server accepts only jobs transferred with compressed data. For clients located in the application directory, the following entries via the oxmljsc.cfg file are used to switch compression on: packed=1packbound=0 The file is found in the respective application directories. You can switch on compressed communication for clients via the relevant oxmljsc.cfg file without switching on the exclusive compressed communication for the server. |
|
|
Verify Windows version |
No (Security\ |
Specifies whether or not clients can only log in under Windows XP or higher. |
|
|
Signature check of modules during loading |
- (Security\ |
Creates a list of modules which are checked for valid signatures as soon as they are started or loaded. The modules in the list are separated by semicolons. Example: ax.exe;axbasics.dll;axavapps.dll |
|
|
Password encryption handling |
Internal and AES algorithm (Security\ |
From version 6.0, enaio® has used Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption. If you have integrated external applications that have not yet been switched over to this encryption method, you can retain the default setting. If this is not the case, it is recommended for security reasons that you select the value 'AES algorithm only' in order that enaio® server accepts only those passwords that are encrypted according to this standard. |
|
|
Edit together |
Yes (Security\ |
||
|
Maximum share time |
60 (Security\ |
Maximum number of days during which documents are shared for joint processing. |
|
|
Log changes to the security system |
No (Security\ |
Additional logging of changes to the security system via the 'Security system' and 'Remote user administration' areas. |
|
Workflow
|
Parameter |
Default (registry entry) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
E-mail notification for work items |
No (Workflow\ |
Specifies whether an additional e-mail will be sent when a work item is placed in a user's inbox. |
|
Support of deadlines |
Yes (Workflow\SupportTimers=1) |
Specifies whether dunning/retention periods will be processed by the workflow engine. |
|
Processing sequence |
2 Workflow\WorkerJobStrategy |
Defines the sequence in which workflow steps are processed by the server: 1 = step age, oldest first, 2 = process age, oldest first, 3 = step age, youngest first. |
The periodic jobs WFM::WorkItemNoti, WFM::WorkerJob, WFM::SpoolerJob, WFM::FileUpdate, and WFM::CheckJob must be enabled for the workflow.
Conversion
|
Parameter |
Default (registry entry) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
FOP path |
- (Conversion\FOPPath) |
Path to the batch file for the FOP (Formatting Object Processor). During server installation, the files are copied to the \etc\fop directory and the path is entered. The installation of JAVA is required, and the environment variable 'JAVA_HOME' must be added to the Java installation path. |
|
FOP timeout |
30000 ms (Conversion\ |
Defines after how many milliseconds the FOP conversion process will be canceled. The conversion may require more time than specified here. |
|
OpenOffice application |
- (Conversion\SOfficePath) |
This property may only be configured upon prior consultation with the consulting team. Path to the soffice.exe OpenOffice application which is used for PDF conversion. This PDF conversion is currently only used for sending W-Documents in PDF format from the client to external recipients. If OpenOffice cannot convert the file format, users will be shown an error message. OpenOffice is not installed automatically. |
|
OpenOffice timeout |
10000 ms (Conversion\ |
This property may only be configured upon prior consultation with the consulting team. Defines after how many milliseconds the PDF conversion process with OpenOffice will be canceled. The conversion may require more time than specified here. |
|
Disable internal image conversion |
No (Conversion\ |
Specifies whether images are converted into PDFs internally or using an external program. Please note that enaio® rendition can only convert single-sided PDF documents. |
|
Fit Quicklooks |
No (Conversion\FitSlides) |
Specifies whether the height and width of Quicklooks or only their height will be adjusted to fit in the Quicklook view; when selecting the second option, the Quicklook may be truncated. |
|
Use SLIDE cache |
Yes (Archive\UseSlideCache) |
Specifies whether renditions are saved in the SLIDE cache of the application server. Independent of this setting, renditions will always be saved to the rendition cache. Yes – Generated renditions will be saved to the SLIDE cache and read from there. No – Generated renditions will not be saved to the SLIDE cache. If a rendition is requested, it will be read from the rendition cache or generated if it does not already exist. |
|
Call renditions using object ID |
Yes (Archive\GetRenditionByID) |
Yes – Existing renditions are called directly from the rendition cache using the object ID without transferring documents from enaio® server to enaio® rendition first. By using this option, network traffic is reduced. No – When requesting a rendition, the document is transferred from enaio® server to enaio® rendition. enaio® rendition reads the rendition from the cache. If the rendition cannot be found in the rendition cache, it will be generated by enaio® rendition as usual; this applies to both options. |
Subscription/Follow-up
|
Parameter |
Default (registry entry) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Send e-mail messages |
Yes (Subscription\SendMails=1) |
Defines whether e-mails will be sent when notifying a subscription/follow-up. |
|
Send e-mails individually |
Send e-mails individually (Subscription\SendSingleMail=1) |
Defines whether e-mails will be sent individually or as a group e-mail when notifying a subscription/follow-up. |
|
Attach index data |
No (Subscription\SendMailWithIndexData=0) |
Defines whether index data will also be sent when notifying a subscription/follow-up. For data protection reasons, it can be necessary to send index data. |
Client Options
|
PDF resolution |
200 DPI (ClientOptions\PdfResolution) |
Defines the resolution in PDF documents which are displayed in the client's internal viewer. The resolution value, which was selected when creating annotations on PDF documents, takes precedence over the value defined here. |
Category: Data
Data in the Data category is divided into further areas. The following settings are available in this category:
Archiving
|
Parameter |
Default (registry entry) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Server type |
Main server (Archive\ServerType=0) |
Main servers can archive documents of other servers; sub-servers can only archive their own documents. |
|
Confirmed archiving |
Not active (Archive\ConfirmedArch=0) |
Controls confirmed archiving. |
|
Free storage space |
50 MB (Archive\FreeMediaSpace=50) |
Indicates the storage space which will be left free on the archiving media. |
|
Cluster size on the jukebox |
1024 KB (Archive\JBClusterSize=1024) |
Defines the default cluster size of the media in the jukebox for calculating free space. |
|
Create backups |
Not active (Archive\MakeBackups=0) |
Specifies whether a backup of the media is stored in the backup directory during archiving. |
|
Pegasus method for calculating free media space |
NTFS method (GetDiskFreeSpaceEx) (Archive\ |
Specifies the method which is used to determine the free space on the archiving media. |
|
Pegasus method for calculating the free space available for the next document to be archived. |
Initial calculation of total free space (Archive\ PegasusFreeSpaceOnly=0) |
The remaining free space for archiving on Pegasus media can be calculated based on the free space initially available or it can be re-calculated each time. |
|
Automatic prearchiving |
Not active (Archive\AutoPreArch=0) |
Defines whether documents of other server groups are handed over before archiving. |
|
Send e-mails when archiving |
No e-mails (Archive\ArchAdminMail=0) |
Specifies which archiving events trigger an e-mail to be sent to the administrator's account. |
|
Maximum number of archiving errors |
1 (Archive\MaxErrorsCount=1) |
Defines after how many errors archiving will be canceled. Insert '0' to not cancel the archiving process. Note that applying a enaio® server patch will reset this value to '1'. |
|
1 (Archive\ExtendedReport=1) |
Specifies whether extended archive logging is activated. Thus, a detailed XML log file will be created. |
|
|
File name of the log file for extended archive logging |
archive%5%7%6%8%9%10.xml (Archive\ReportName) |
Specifies the path and the file name of the log file for extended archive logging. The file will be written to the \server\log directory. %5 stands for the year, %7 for the month, %6 for the day, %8 for the hour, %9 for the minute, and %10 for the second. |
|
Delete archived documents |
Do not delete |
Specifies whether files on media will also be deleted if archived documents are permanently deleted if possible. The current retention time on the archive is taken into account with the 'Delete' option both when Dearchiving and when deleting documents from enaio® and prevents deletion there. In this case, neither archiving nor deleting the documents is possible. |
|
Hash value check during archiving/dearchiving |
yes (Archive\ReadAfterWrite=1) |
Defines whether to check hash values during archiving/dearchiving processes. This ensures error-free transfer, though it will have an impact on performance. This check is independent of the functions for document integrity. |
|
Archive object definition |
Yes (Archive\ArchiveObjDef=1) |
Specifies whether to additionally archive the corresponding object definition during each archiving process. If this option is disabled, you will need to ensure that the index data and the corresponding data model match the data in your process documentation. |
|
Retention times |
Unix time range (Archive\RetentionBehavior2038=1) |
Specifies the valid range for retention times. 32-bit systems may require you to limit the valid retention time. To do so, select the Unix time range (1). As a result it will be impossible to specify retention times beyond 19 January 2038. If retention times can be specified without constraint, select the continuous time range (2). If you use an older version of NetApp archives, select the extended NetApp time range (3). As a result, the valid time range for retention times extends to 19 January 2071. For NetApp archives versions 9.10 and later, the continuous time range can be selected. Then values > 2071 can also be entered. |
| Transfer retention times |
No (Archive\RetentionTimeOfLinks=0) |
Retention times are transferred to reference documents. |
To guarantee easy configuration and secure operation, enaio® provides tools and resources for different certified archive storage systems. Nevertheless, keep in mind to follow the configuration steps described in the respective interface manuals.
It is therefore advisable to coordinate, implement, document, and test the planning of retention periods, the selection of an archive storage system and its configuration, the configuration of retention times as well as necessary archive storage system settings in enaio®, and the correct configuration and execution of archiving processes in enaio® within the project with our consulting department.
Database Parameters
|
Parameter |
Default (registry entry) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Data source |
askrn (DataBase\Source=askrn)) |
Indicates the ODBC data source name for access to the database server. This entry is specified during installation, written to the registry, and cannot be modified. |
|
Parser for database queries |
ODBC parser (DataBase\ |
The parser is predefined. |
|
Database schema |
- (DataBase\Schema) |
Specifies the name of the database scheme. The name is used to determine table names, table indexes, and column names. This entry is left empty if no custom schema is explicitly specified for the database. |
|
Maximum DB field length |
2000 (DataBase\DBMaxChar=2000) |
Indicates the maximum string length of a character field in the database. This value depends on the database in use and can be changed accordingly. |
|
Pool size for job threads |
5 (DataBase\PoolJobThreads=5) |
Indicates the number of DB connections allowed in the pool of job threads. You can enter a value between '1' and '64'. It is recommended that you do not modify the value. |
|
Pool size for read threads |
5 (DataBase\PoolReadThreads=5) |
Indicates the number of DB connections allowed in the pool of read threads. You can enter a value between '1' and '64'. The capacity can be viewed in the area Extended administration > Database pool > Read threads. |
|
Replace CR character with CRLF |
Replace (DataBase\ReplaceCR=1) |
Defines whether CR characters in the database are replaced with CRLF characters for display purposes when reading strings. |
|
50000 (DBPipe\MaxHits=50000) |
Maximum number of hits of SQL Select statements for queries from enaio® applications. The maximum number of hits for enaio® webclient is set via the enaio® webclient configuration. This setting also affects the 'Full text indexing' automatic actions and limits the number of documents processed there. |
ADO Database Access
SQL queries access the database via ADO.
|
Parameter |
Default (registry entry) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Execution of SQL commands (write access) |
Allow execution (ADO\ExecuteCommands=1) |
Specifies whether to allow write access to the database when using the ADO database access with SQL queries. Set the value to 'Do not allow execution' in order to close this potential security gap. |
|
Name of the OLE DB provider |
MSDASQL (ODBC) (ADO\Provider=MSDASQL) |
Indicates the name of the OLE DB database provider. |
|
Cursor type |
Forward only (ADO\CursorTypeSelect=0) |
Cursor type when opening an ADO query. Default to 7.50: 'Dynamic'. This cursor type is not changed when patches are applied. We recommend the cursor type 'ForwardOnly'. If necessary, check whether a change is possible. |
Please contact our consulting team if you encounter problems with SQL queries.
Category: Engines
All engines are listed here. The engine for the workflow is enabled automatically. If needed, the MED engines must be enabled manually.
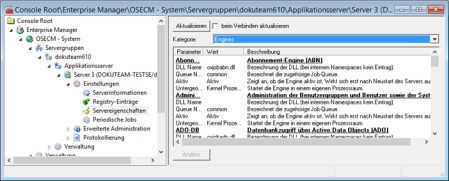
Engines that are not needed can be disabled. An active engine that is not needed only places an extra load on the system when executing periodic jobs.
The workflow engine is assigned periodic jobs, which will also be enabled.
Changes only take effect after the server is restarted. It is possible to load or unload engines during runtime from the Extended administration > Set up > Engines area.
A queue name is specified for each engine. It is possible to set up new job queues for engines or to increase the number of threads. The job queues' capacity can be viewed under Advanced administration > Monitoring > Job queues while you can display and edit the parameters for queues in the Queues category.
Engines are run in the kernel process space. They can be started in an individual process space for error analysis purposes. It is recommended that you only make changes upon prior consultation with the support team.
This data is managed in the server registry. A key containing the required strings and values is created for each engine beneath the NameSpaces registry key.
Category: Integrity
The settings available in the Integrity category allow you to activate mechanisms which helps you find errors on archiving media and detect direct accesses to document files.
|
Parameter |
Default (registry entry) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Hash check before archiving |
Do not check (integrity\HashNeeded=0) |
The hash value can be checked prior to the archiving process. |
|
Signature check before archiving |
Do not check (integrity\SignatureNeeded=0) |
Additionally, the signature of the hash value can be checked prior to archiving a document. |
|
Hash check created before document request |
Do not check (integrity\CheckDocHashOnRequest=0) |
The hash value can be checked whenever a document is requested. If the check is activated, the hash value will also be checked after dearchiving. |
|
Signature check before document request |
Do not check (integrity\CheckDocSigOnRequest=0) |
Additionally, the signature of the hash value can be checked whenever a document is requested. |
|
Automatic signature creation |
Do not create (integrity\Sign=0) |
Every hash value is generated while creating or editing a document file is signed. |
|
Signature errors treated as severe |
Do not cancel (integrity\ErrorAsFailure=0) |
Errors which occur while creating or checking a signature will only cancel an action if you enter the 'Cancel' value. |
|
Signature module |
- (integrity\DllName=oxsignos.dll) |
Only the 'oxsignos.dll' module can be used for signing. Do not change this value. |
|
Parameters of the signature module |
- (integrity\Parameters=algo=1) |
Do not change this value. |
|
Signature code |
- (integrity\Code) |
Subsequent signing of document files requires a signature code. |
|
Period of validity of the signature code |
- (integrity\CodeExpires) |
The validity period of the signature code for subsequent signing must be entered here. |
Category: Periodic Jobs
Registry entries control the setup of jobs periodically executed by the server during installation.
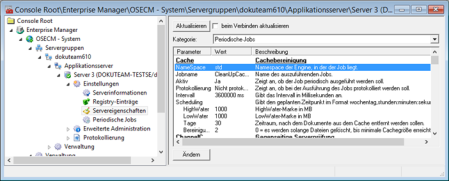
This configuration area enables you to view all periodic jobs, allowing you to enable or disable them and to change their parameters.
New periodic jobs are created in the Settings > Periodic jobs area.
In most cases, these settings can be left as they are.
The following periodic jobs are set up:
- Server ping
The server periodically writes a date to the database that other servers use to check whether or not the server is active. If not, the 'Server monitoring' periodic job enables other servers to release sessions of inactive servers.
The period of job repetition is specified in milliseconds; default: 60000 ms.
- Server monitoring
By use of the database entry, the server checks whether other servers are still active and, if necessary, releases sessions of inactive servers.
The period of job repetition is specified in milliseconds (default: 60000 ms). This period value must not be less than the period specifying the server ping (see above).
- ChannelCheck
The server periodically sends information to the database on whether other servers can be reached via the TCP connection. All servers which are not available are flagged and will not be sent further jobs. Specify with the 'UnreachableToo' parameter whether or not to keep on trying to connect to these servers.
- ClientPing
The server sends a ping to the clients.
This general job can be extensively configured. You can specify which computers and applications are sent a ping.
It is recommended to set up a periodic job that consistently sends a ping to all computers.
The following parameters can be specified:
|
Computer |
The name of the computer where the message will be sent. If the entry is left empty, a ping will be sent to all computers. |
|
GUIDs |
This parameter is used internally and must be left empty. |
|
Info |
This parameter is used internally and must be left empty. |
|
Instance |
Indicates the enaio® application to which a ping is sent. Example: ax If the entry is left empty, a ping will be sent to all application instances. |
|
Message |
ping – a ping is sent. Additional message types are available but not suited as periodic jobs. |
|
Text |
Leave this entry blank. |
|
Users |
Leave this entry blank. |
The Computer, Instance, and User parameters are combined using the logical AND when executed. Only one value can be entered for each parameter. No entry means 'send to all'.
The Advanced administration > Monitoring > Connections > Active clients area allows you to send messages directly to clients or close them.
Parameters are preset for sending messages to prevent messages from being placed in the message queue if there is already a specified number of unanswered messages there:
| Parameter | Default | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Notifications\MaxNotificationMessages | 2000 |
Maximum number of messages in the queue Further messages will be ignored. Set '0' to disable the function. |
| Notifications\MaxNotificationMessagesPerSession |
0 |
Maximum number of messages in the queue for a session The session will be closed when the number and timeout are exceeded. Set '0' to disable the function. |
| Notifications\NotificationTimeout | 300 | Timeout in seconds for 'MaxNotificationMessagesPerSession' |
- SessionCheck
The server checks periodically or at a defined interval whether the tables for resource and session allocation contain entries which do not correspond to the sessions linked to the server anymore, and deletes all sessions which are inactive over an indicated time period.
- Cache
The server periodically clears the cache area.
Cache maintenance can also be set up as an automatic action (see ''Cache Maintenance' Action'). Job parameters are also discussed in this chapter.
- Follow-up
The server periodically checks whether users have received follow-ups and informs the clients.
In multi-server systems, a server can only inform the clients that are connected to the server.
- Subscription
The server periodically checks whether subscriptions are available for users and informs the client.
In multi-server systems, a server can only inform the clients that are connected to the server.
- SessionDropNotActive
The server periodically checks whether there are sessions which have been inactive for 72 hours. If so, these sessions will be deleted. The activity duration for sessions can be changed; however, it cannot be shorter than eight hours, otherwise errors will occur.
- Workflow check
The server periodically checks whether dunning or retention times trigger changes in workflow processes. Activities affected by retention periods are activated after expiration, and those with expired deadlines are marked as late and have their defined action executed.
The period of job repetition is specified in milliseconds (default: 60000 ms). Normally, you can considerably increase the period value.
If you neither use dunning nor retention periods, you can deactivate this job.
- Workflow worker
The server executes workflow processes. Activities are started or ended by this job.
The period of job repetition is specified in milliseconds (default: 3000 ms). In case of a small number of processes, the period value can be increased.
- Workflow notification
The server periodically checks whether workflow processes exist and informs all connected clients about changes in the inbox.
The period of job repetition is specified in milliseconds (default: 2,000 ms). Normally, you can increase the period value. It must not be decreased.
The server periodically checks whether report jobs exist. The period for the job is specified in milliseconds; default: 6000 ms.
If you do not use reports, you can deactivate this job.
- CheckExpires
The server periodically checks when license keys expire and an e-mail will be sent to the administrator's account.
The default daily execution time of this job is every four hours. The Days parameter specifies the number of days before a license key expires that an e-mail will be sent. By default, the e-mail will be sent 14 days before the license expires.
- CheckDiskSpaceData
The server periodically checks the capacity of the drive containing the work directory.
The period of job repetition is specified in milliseconds (default: 360000 ms). The parameter Disk indicates the logical drive; InformAdmin – Yes defines that, if the remaining capacity drops below the value of the parameter MinSpace, an e-mail will be sent to the administrator's account.
The default value for the MinSpace parameter is set to '0,' which means that it equals to the value of the Free hard disk space parameter set in the Server properties > Category: General area.
- CheckDiskSpaceLog
The server periodically checks the capacity of the drive containing the directory into which the server saves its logs.
The period of job repetition is specified in milliseconds (default: 360000 ms). The parameter Disk indicates the logical drive; InformAdmin – Yes defines that, if the remaining capacity drops below the value of the parameter MinSpace, an e-mail will be sent to the administrator's account.
- CheckDiskSpaceRoot
The server periodically checks the capacity of the drive containing the server directory.
The period of job repetition is specified in milliseconds (default: 360000 ms). The parameter Disk indicates the logical drive; InformAdmin – Yes defines that, if the remaining capacity drops below the value of the parameter MinSpace, an e-mail will be sent to the administrator's account (see above).
- GetProcessInfo
System load is determined and logged periodically. A separate channel is required for logging (see 'Logging the System Load').
- ProcessSlideCPMessages
The server checks regularly whether messages concerning the creation of renditions are available.
The period of job repetition is specified in milliseconds (default: 60000 ms). The parameter QueueNames indicates one or more names of the queues whose messages are processed by the job.
Furthermore, you can specify the following optional parameters in the Settings > Periodic jobs > Edit area:
|
ConcurrentJobCount |
0 – no restriction. Even if the parameter is not specified, the number of parallel jobs is not limited. > 0 – number of jobs that can be executed in parallel. All further jobs are terminated immediately. |
The namespace of a job defined by the setup program is used to automatically determine in which queue it is executed. Use the optional $$$QueueName$$$ parameter, which can be entered for all jobs in the Settings > Periodic jobs > Edit area, to specify a queue in which the job is executed. You can only specify queues that were created by the setup.
Periodic jobs are only executed when the related engine is active. Changes are applied immediately; restarting the engine is not required.
By double-clicking an entry you can open its settings dialog. The JobName and Namespace parameters may not be edited.
This data is managed in the server registry. The keys for every periodic job are listed together with the required strings and values under the Batches key.
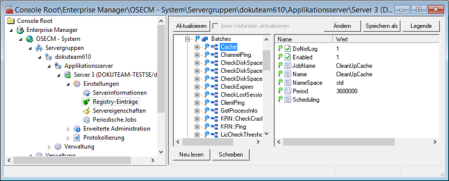
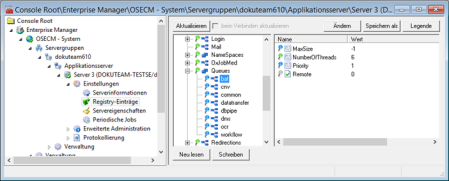
Category: Queues
All queues are listed in this area.
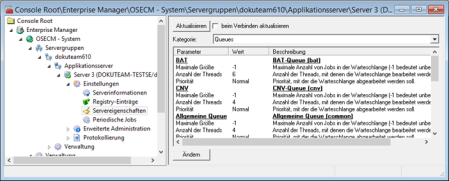
You can individually configure the maximum number of jobs in a queue, the number of threads and the priority for each queue.
The maximum number of jobs is by default set to '-1' (unlimited). The priority of all queues is set to 'normal', and the number of threads varies.
In most cases these settings can be left as they are. In the Extended administration > Monitoring > Queues area you can view the capacity of the queues. For heavily loaded queues you can either increase the number of threads or create new queues for engines.
The BAT queue is the default queue for CPB batch processing. Processes running in the background or processes with long runtimes could slow down the enaio® platform when it is running in standard operating mode. It is recommended to outsource these processes to the BAT queue which is equipped with 6 threads by default in order to improve load balancing.
The priority according to which the operating system processes the threads of the OCR queue can be reduced because time-consuming OCR processes can slow down the rest of the system.
If you are using numerous and complex workflow processes and your computer is equipped with high-performance hardware, you can increase the number of threads of the workflow queue to six or eight.
This data is managed in the server registry. A key and the required strings and values will be generated for each queue under the Queues key.
Category: Services
Data that falls in the Services category are divided into further areas.
The content processing bus and rendition cache, the core services enaio® contentviewer, enaio® documentviewer, enaio® appconnector (enaio® contentviewer), enaio® webservices, enaio® exchange, and up to ten additional web services (in the form of dashlets) are configured in these areas.
The core services – enaio® contentviewer, enaio® documentviewer, and enaio® contentviewer – are used to flexibly display documents as well as document and index data, and they can also be integrated into enaio® client and enaio® webclient.
The service endpoints entered here are transferred automatically to the client registry when enaio® client is installed and can be read from other components. Changes to the service endpoints, however, are not automatically transferred to the client registry. To synchronize the client registry with the values in the server registry, perform an update of the client installation.
Content Processing Bus
|
Parameter |
Default (registry path/entry) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Use content processing bus |
Yes (CPB\RenditionExport) |
Defines whether the content processing bus is used. |
|
Queues for rendition export |
RENDITION (CPB\ |
Names for the rendition export queues. Use a semicolon to separate multiple names. |
|
Index data export queues |
FULLTEXTIDX (CPB\ |
Names for the index data export queues. Use the semicolon to separate multiple names. |
|
Queues for document export |
FULLTEXTDOC (CPB\ |
Names for the document export queues. Use the semicolon to separate multiple names. |
|
Queues for thumbnail export |
SLIDE (CPB\ |
Names for the thumbnail export queues. Use the semicolon to separate multiple names. |
|
Queues for page count export |
PAGECOUNT (CPB\ |
Names for the page count export queues. Use the semicolon to separate multiple names. |
Rendition Cache
|
Parameter |
Default (registry path/entry) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Service endpoint |
- (Services\RenditionCache\API) |
URL under which the service is accessible. |
|
Service endpoint for direct access |
- (Services\RenditionCache\ |
The URL specifies the server that the rendition cache is running on. |
Contentviewer
|
Parameter |
Default (registry path/entry) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Home URL |
- (Conversion\ |
URL for parameterized service access. Schema: http://<gateway>/applet/contentviewer/index.html?osid={OBJECTIDENT} When opening files, enaio® contentviewer displays the detailed preview with index data and basic parameters by default. To display the content preview first, add the home URL as shown here: http://<gateway>/applet/contentviewer/index.html?osid={OBJECTIDENT}&focusIndexData=false |
|
Service endpoint for direct access |
- (Conversion\API_DIRECT) |
The URL specifies the server that the service is running on. |
Documentviewer
|
Parameter |
Default (registry path/entry) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Home URL |
- (Services\ |
URL for parameterized service access. Default: http://<gateway>/applet/pdfview/viewer.html?osid={OBJECTIDENT}&pagecount={pagecount}&sessionguid={sessionguid}&servername={servername}&serverport={serverport}&objecttype={objecttype}&q={searchterm} |
|
Service endpoint |
- (Services\DocumentViewer\API) |
URL under which the service is accessible. |
|
Service endpoint for direct access |
- (Services\DocumentViewer\API_DIRECT) |
The URL specifies the server that the service is running on. |
|
Home URL for thumbnails |
- (Services\ |
URL for enaio® documentviewer document previews, e.g., when using the 'Send e-mail' feature in enaio® client. Thumbnails of the first page of documents which are attached to an e-mail will be inserted into the e-mail body whenever an e-mail is sent using Microsoft Outlook. |
|
Job directory |
- (Conversion\ |
The UNC path for enaio® documentviewer where the job files are stored. These jobs are stored in the …\osdocumentviewer\data\jobs standard directory if no other path was specified on the config.properties administration page. When the CPB is used, messages – not jobs – are used for communication; it is therefore not necessary to specify the directory. |
Appconnector
|
Parameter |
Default (registry path/entry) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Home URL |
- (Services\ |
Basic URL of enaio® appconnector. |
|
Service endpoint |
- (Services\AppConnector\API) |
URL under which the service is accessible. |
|
Service endpoint for direct access |
- (Services\AppConnector\ |
The URL specifies the server that the service is running on. |
Web service
|
Parameter |
Default (registry path/entry) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Service endpoint |
- (Services\OSWS\API) |
URL under which the service is accessible. |
|
Service endpoint for direct access |
- (Services\OSWS\API_DIRECT) |
The URL specifies the server that the service is running on. |
Exchange
|
Parameter |
Default (registry path/entry) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Service endpoint |
- (Services\OSExchange\API) |
URL under which the service is accessible. |
|
Service endpoint for direct access |
- (Services\OSExchange\API_ DIRECT) |
The URL specifies the server that the application is running on. |
IMAP
|
Parameter |
Default (registry path/entry) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Service endpoint |
- (Services\IMAP\API) |
URL under which the service is accessible. |
|
Service endpoint for direct access |
- (Services\IMAP\API_DIRECT) |
The URL specifies the server that the service is running on. |
Full Text
|
Parameter |
Default (registry path/entry) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Service endpoint |
- (Services\Fulltext\API) |
URL under which the service is accessible. |
|
Service endpoint for direct access |
- (Services\Fulltext\API_DIRECT) |
The URL specifies the server that the service is running on. |
Gateway
|
Parameter |
Default (registry path/entry) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Service endpoint |
- (Services\Gateway\API) |
URL under which the service is accessible. |
|
Service endpoint for direct access |
- (Services\Gateway\API_DIRECT) |
The URL specifies the server that the service is running on. |
Detailsviewer
|
Parameter |
Default (registry path/entry) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Home URL |
- (Services\Detailsviewer\URL) |
URL for parameterized service access. Default: http://<gateway>/applet/detailsviewer/index.html?osid={OBJECTIDENT}&sessionguid={sessionguid} |
|
Service endpoint |
- (Services\Detailsviewer\API) |
URL under which the service is accessible. |
|
Service endpoint for direct access |
- (Services\Detailsviewer\API_DIRECT) |
The URL specifies the server that the service is running on. |
Discovery
|
Service endpoint for direct access |
- (Services\Discovery\API_DIRECT) |
The URL specifies the server that the service is running on. |
Dashlet Error
|
Home URL |
http://www.optimal-systems.de (Services\Dashlet_ErrorURL) |
This page can be shown in the event of a dashlet error or if a dashlet is not available. |
Dashlets 1–10
|
Parameter |
Default (registry path/entry) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Home URL |
- (Services\Dashlet1_URL) (Services\Dashlet2_URL) … |
Home URL for dashlets 1–10. Structure: http(s)://<gateway>:<port>/<dashlets>/<filename> |
|
Title |
Dashlet 1 (Services\Dashlet1_Title) Dashlet 2 (Services\Dashlet2_Title) … |
Window title and tooltip to be shown in the workspace. Dashlet titles can be localized. |
|
Icon ID |
0 (Services\Dashlet1_IconID=0) |
ID of an icon that is integrated using enaio® editor. |
|
Load at start |
No (Services\Dashlet1_LoadOnStartup) (Services\Dashlet2_LoadOnStartup) … |
Dashlet content will be loaded when starting the client. |
Dashlets do not need to be numbered sequentially. This makes it easy to disable individual dashlets.
 areas. Use the toolbar to show all hidden areas at once:
areas. Use the toolbar to show all hidden areas at once:
