Kerberos Authentication
User names can be managed in enaio® on the basis of the UPN ('user principal name': for example, 'name@mydomain.com') or the SAM user name ('security accounts manager': for example, 'name'). In both cases, user authentication can be carried out using Kerberos in enaio® via Windows.
From a technical standpoint, NTLM always requires the SAM as the authentication mechanism, whereas Kerberos always requires the UPN.
The identification of the user to be logged in is configured for Kerberos in enaio® enterprise-manager via the Login/name resolution (Kerberos) parameter. If this parameter is set to UPN, then all enaio® users must comply with the UPN form. If this parameter is set to SAM, the SAM needs to be used for all users. The corresponding registry key is called QueryNamesMethod in the server registry and it has the values 0/1 (SAM/UPN).
If Kerberos is configured correctly for Windows, the other settings are made in the configuration of enaio® server in enaio® enterprise-manager.
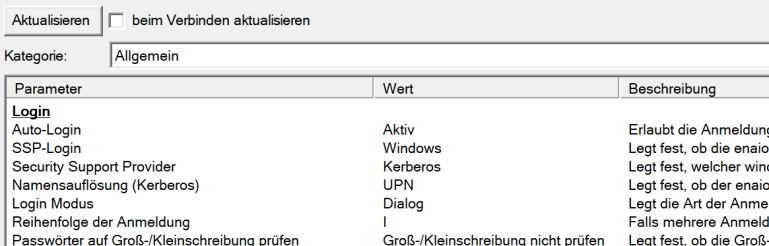
Here, Auto login is set to Active and SSP login is set to Windows so that the authentication of the client applications for enaio® server is carried out via Windows and the server-internal parameter Login order is not used. The security support provider is set to Kerberos and the name resolution (Kerberos) needs to be selected according to the names of the users in the system.
| Parameter | Value | Value in the server registry |
|---|---|---|
| Auto login | Active | Schema/Login/Auto login : 1 |
| SSP login | Windows | Schema/Login/NTLM login : 1 |
| Name resolution (Kerberos) | UPN | Schema/Login/QueryNamesMethod : 1 |
| Security Support Provider | Kerberos | Schema/Login/Support provider : Kerberos |
Furthermore, the user account for the enaio® server service needs to be a domain account for Kerberos authentication. A local system user account that is normally used is not suitable. The domain account must be granted sufficient rights to run the service. In addition, a suitable SPN (service principal name) needs to be assigned for this user account in the domain.
Example: enaio/myserver.mydomain.com:4000 myserver
myserver.mydomain.com is the computer on which enaio® server is installed. You need to have entered the fully qualified name, including port, here.
In the asinit.cfg configuration file, which defines the target server in the client installations, the fully qualified name of the corresponding server including port needs to be specified on the enaio® client side instead of the usual IP/computer name with port. Similar to the above example, the result here is:
[ARCHIV]
Comstring=myserver.mydomain.com#4000Once these settings have been made and the asinit.cfg configuration file has been distributed across all client-side installations, the login for enaio® client, the administrative components, and enaio® capture can be carried out via Kerberos.
enaio® enterprise-manager Continues to use the Windows-based login, which means that a login exception needs to be defined for this application.
 areas. Use the toolbar to show all hidden areas at once:
areas. Use the toolbar to show all hidden areas at once:
